Ambulatory Electro-
cardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnostic technique that detects and examines the electrical activity of the heart for any abnormalities. An ECG converts the electrical activity of the heart into line tracings that physicians may use to diagnose abnormal heart rates and rhythms.
Q & A
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnostic technique that detects and examines the electrical activity of the heart for any abnormalities. An ECG converts the electrical activity of the heart into line tracings that physicians may use to diagnose abnormal heart rates and rhythms.
Electrocardiograms are utilized to:
- Check the electrical activity of the heart
- Determine the source of chest symptoms, which might be the manifestation of heart attacks or lung clots
- Determine the cause of heart disease symptoms
- Determine the thickness of the chambers of the heart.
- Evaluate the efficacy of treatment or the occurrence of adverse effects
- Determine the etiology of palpitations
- Evaluate for genetic abnormalities if there is an extensive family history of cardiac problems.
How is this performed
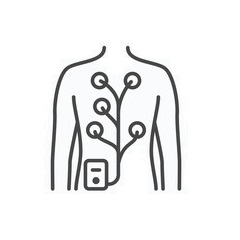
A skilled technician performs an electrocardiogram (ECG), and the doctor will evaluate its results. Several electrodes will be placed to each arm, leg, and chest throughout the process, after the regions have been thoroughly cleansed. The electrodes will then assess the electrical activity of the heart. The patient will be instructed to lie motionless and breathe normally, or they may be instructed to hold their breath.
An ECG is non-harmful and non-painful since no actual electricity is sent into the body during the treatment.
The doctor will next discuss the results of the ECG with the patient. Abnormal findings may have several interpretations, including:
- cardiac arrhythmias
- alterations or damage to cardiac muscle
- alterations in sodium and potassium in the bloodstream
- congenital cardiac abnormality
- fluid or swelling in the sac that surrounds the heart
- inflammation of the heart (myocarditis)
- a previous or present heart attack
- pulmonary embolism and it’s strain on the heart.
24- or 48-hour ECG when the patient will be forced to wear an electronic recorder for 24/48 hours. Exercise ECG recorded while the patient is exercising to determine how the heart responds to stress (also called a Holter monitor or ambulatory ECG)
Cardiac event recorder that keeps track of a patient’s heartbeat over an extended period of time.